
Science & Tech
James Webb Space Telescope reveals stunning first images of deep-space
A cosmic deep dive, these photographs are the deepest and sharpest full-colour images of the universe yet
- 1067 words
- 5 minutes
This article is over 5 years old and may contain outdated information.
Science & Tech
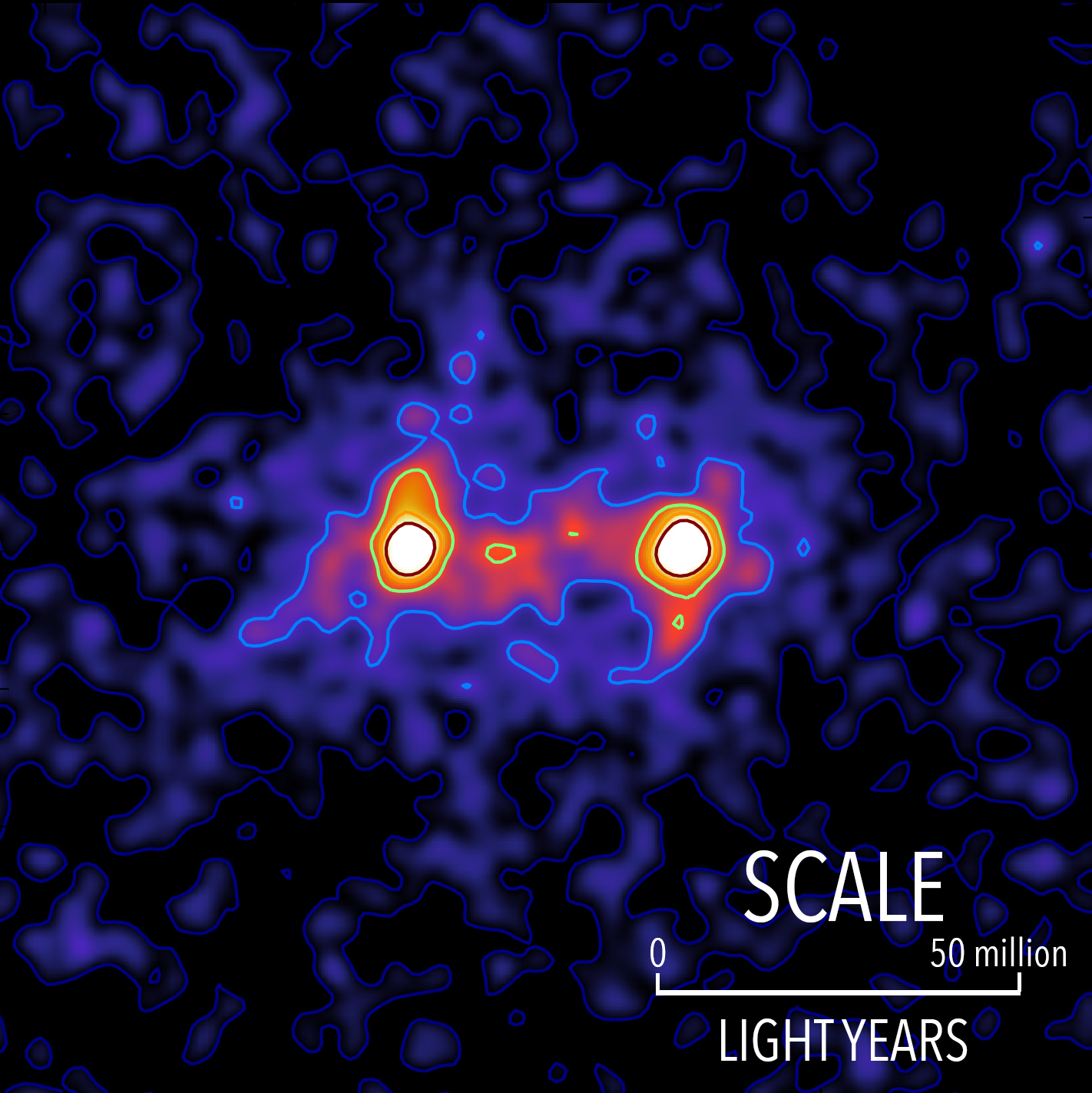
In the time since dark matter was first hypothesized in 1922, it’s been a substance of mere theory; the matter doesn’t shine, reflect or absorb light, so astronomers could not see it. Until now.
Astronomers at the University of Waterloo have published the first image of dark matter. It confirms theories that there’s a web of dark matter between galaxies.
Despite the challenges in detecting dark matter, professor Mike Hudson and then-masters student Seth Epps found a way to map an image of the substance anyway. It relies on a process called gravitational lensing. When astronomers take photos of galaxies, different types of matter, like planets, stars or dark matter, can get between Earth and the galaxy. This matter causes distortion in the image.
“If you had a galaxy that would normally be perfectly round,” Hudson said, “the presence of the matter in front of it can stretch it and make it look sort of elliptical.”
The distortions tend to be predictable, so Hudson, Epps and a team of researchers working with the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope measured the distortions between many pairs of galaxies to get an idea of what dark matter looks like. The final image is a composite of images taken from 12,000 pairs about 4.5-billion light-years away.
They learned that dark matter is sort of like a spider web, but instead of being flat Hudson said it’s “more like a sponge structure.”
Within that sponge, in the “knots in the web, where the galaxies are,” Hudson said there are even thinner filaments of dark matter. There may be even smaller galaxies within them.
From here, he and the other astronomers will be looking more deeply into the data to see if the theory holds up in the face of more quantitative analysis, with calculations and simulations.
They’ve also started to collect more, and hopefully better data, with the Canada-France Imaging Survey. This will look at a bigger part of the sky than the previous research.
Although the image hasn’t brought any new theories to light—yet—Hudson is still in awe of the work they’re doing.
“Occasionally I take a step back and I think, “You know, this is amazing: We’re making pictures of dark matter. Who would have thought that was possible?’”
Are you passionate about Canadian geography?
You can support Canadian Geographic in 3 ways:

Science & Tech
A cosmic deep dive, these photographs are the deepest and sharpest full-colour images of the universe yet

Science & Tech
With help from Canadian scientists, this dark universe hunter aims to study why the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate

Science & Tech
As geotracking technology on our smartphones becomes ever more sophisticated, we’re just beginning to grasps its capabilities (and possible pitfalls)

Mapping
We know of Canada’s beauty from the ground; the open lakes, towering trees and jutting rocks that define the wild North.What about from above?We get glimpses…